|
Technological innovation and efficiency improvements are often cited as pathways to decouple growth in material use from economic growth. While technology undoubtedly has a crucial role to play in the transition to a sustainable world, it is constrained by fundamental physical principles and pragmatic economic considerations.
Examples abound. The engine efficiency of airplanes has improved little for decades since they have long been operating close to their theoretical peak efficiency. Likewise, there is a hard limit on the efficiency of photovoltaic cells of about 35 percent because of the physical properties of the semiconductors that constitute them; in practice few exceed 20 percent for economic and pragmatic reasons. The power generation of large wind farms is limited to about one watt per square meter as a simple yet utterly unavoidable physical consequence of wake effects. The awesome exponential increase in computing power of the past five decades will end by about 2025 since it is physically impossible to make the transistors on the computer chip, already roughly 5 percent of the size of the coronavirus, much smaller.
Whether it is principles of classical, quantum or solid state physics or thermodynamics, each places different but inexorable constraints on technological solutions. Basically, physical principles that have allowed incredible technological leaps over the past century also inevitably limit them. We might consider that extensive recycling of materials would offset efficiency limits. Recycling is crucial; however, while glass and metals can be recycled almost indefinitely without loss of quality, materials such as paper and plastic can be recycled only a few times before becoming too degraded.
Additionally, recycling itself may be an energy- and materials-intensive process. Even if physical laws could be broken (they cannot) to achieve recycling with 100 percent efficiency, added demand from the imperative for economic growth would necessarily require virgin materials. The key point is that efficiency is limited by physics, but there is no sufficiency limit on the socioeconomic construct of demand.
Unfortunately, the situation is even more dire. Economic growth is required to be exponential; that is, the size of the economy must double in a fixed period. As referenced earlier, this has driven a corresponding increase in the material footprint. To understand the nature of exponential growth, consider the EV. Suppose that we have enough (easily extractable) lithium for the batteries needed to fuel the EV revolution for another 30 years. Now assume that deep-sea mining provides four times the current amount of these materials. Are we covered for 120 years? No, because the current 10 percent rate of growth in demand for lithium is equivalent to doubling of demand every seven years, which means we would only have enough for 44 years. In effect, we would cause untold, perhaps irreversible, devastation of marine ecosystems to buy ourselves a few extra years supply of raw materials.
Exponential growth swiftly, inevitably, swamps anything in finite supply. For a virus, that finite resource is the human population and in the context of the planet it is its physical resources.
The inescapable inference is that it is essentially impossible to decouple material use from economic growth. And this is exactly what has transpired. Wiedmann et al., 2015 did a careful accounting of the material footprint, including those embedded in international trade, for several nations. In the 1990 2008 period covered by the study, no country achieved a planned, deliberate economywide decoupling for a sustained length of time. Claims by the Global North to the contrary conceal the substantial offshoring of its production, and the associated ecological devastation, to the Global South.
Recent proposals for ecocidal deep-sea and fantastical exoplanetary mining are an unsurprising consequence of a growth paradigm that refuses to recognize these inconvenient truths.
WHAT IS SUSTAINABILITY?
These observations lead us to a natural minimum condition for sustainability: all resource use curves must be simultaneously flatlined and all pollution curves simultaneously extinguished. It is this resource perspective that allows us to see why EVs may help offset carbon emissions yet remain utterly unsustainable under the limitless growth paradigm.
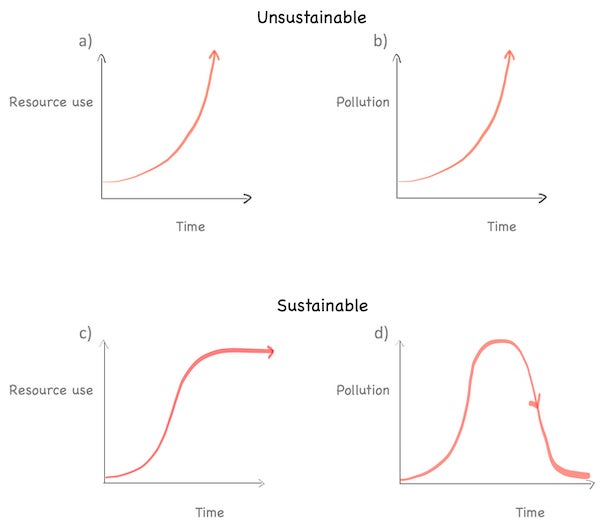 Sustainability from a resource perspective: Exponentially rising resource use and pollution (a and b) are unsustainable. We define sustainability as flatlined resource use (c) and extinguished pollution (d). Credit: Aditi Deshpande
Sustainability from a resource perspective: Exponentially rising resource use and pollution (a and b) are unsustainable. We define sustainability as flatlined resource use (c) and extinguished pollution (d). Credit: Aditi Deshpande
|